Market Implications of Latest CPI, PPI, Unemployment, and Retail Sales Data Release

Recent releases of some Federal Reserve data in February 2025 brought us a very elaborate picture of the key economic indicators such as steady consumer activity, sustaining price and inflation pressures, and relative optimism of businesses about making a turnaround. Here we will explore in depth what the latest figures revealed through the Consumer Price Index (CPI), Producer Price Index (PPI), latest Unemployment Data, and Retail Sales Data release, mean for the overall market sentiment and the investors at large.
Fresh Consumer Price Index data shows prices climbed 0.5% between December and January, slightly outpacing forecasts. When you compare this figure to last year’s, the 3.0% increase weighs slightly bigger than December’s 2.9% figure. This clearly shows that instead of fading away steadily, concern over inflation remains constant. Apart from posing some challenges for policymakers, the impact is visible in the growing cost in sectors like housing and transportation.
Businesses, too, face mounting input expenses. Producer prices, which refers to the price companies pay for materials and services, increased by 0.4% in January. This is more or less the continuation of the trend that started late last year. If we look at the movement in the cost curve during the past twelve months, the increased percentage of these costs has been 3.5% and this is the highest annual increase since the first quarter of 2023. The two major driving forces responsible for this are respectively energy markets and agricultural supply chains. To speak more particularly, volatility in oil prices and disruptions caused by some weather conditions and natural calamities played an instrumental role in pushing up the production budgets.
Despite all these challenges, we have some good news from the employment scenario. New unemployment claims data has a sharp downturn that clearly shows the reluctance of employers to reduce the human capital load while facing economic constraints. This resilience matters because paychecks most of the time boost consumer spending. In December only retail sales experienced 0.4% growth after a quite overwhelming 0.8% growth rate in November. So, seemingly, the momentum is on with some critical restraints. In overall measures, this signals cautious optimism.
A Quick Recap of Federal Reserve Data Releases Between February 12 to 14, 2025
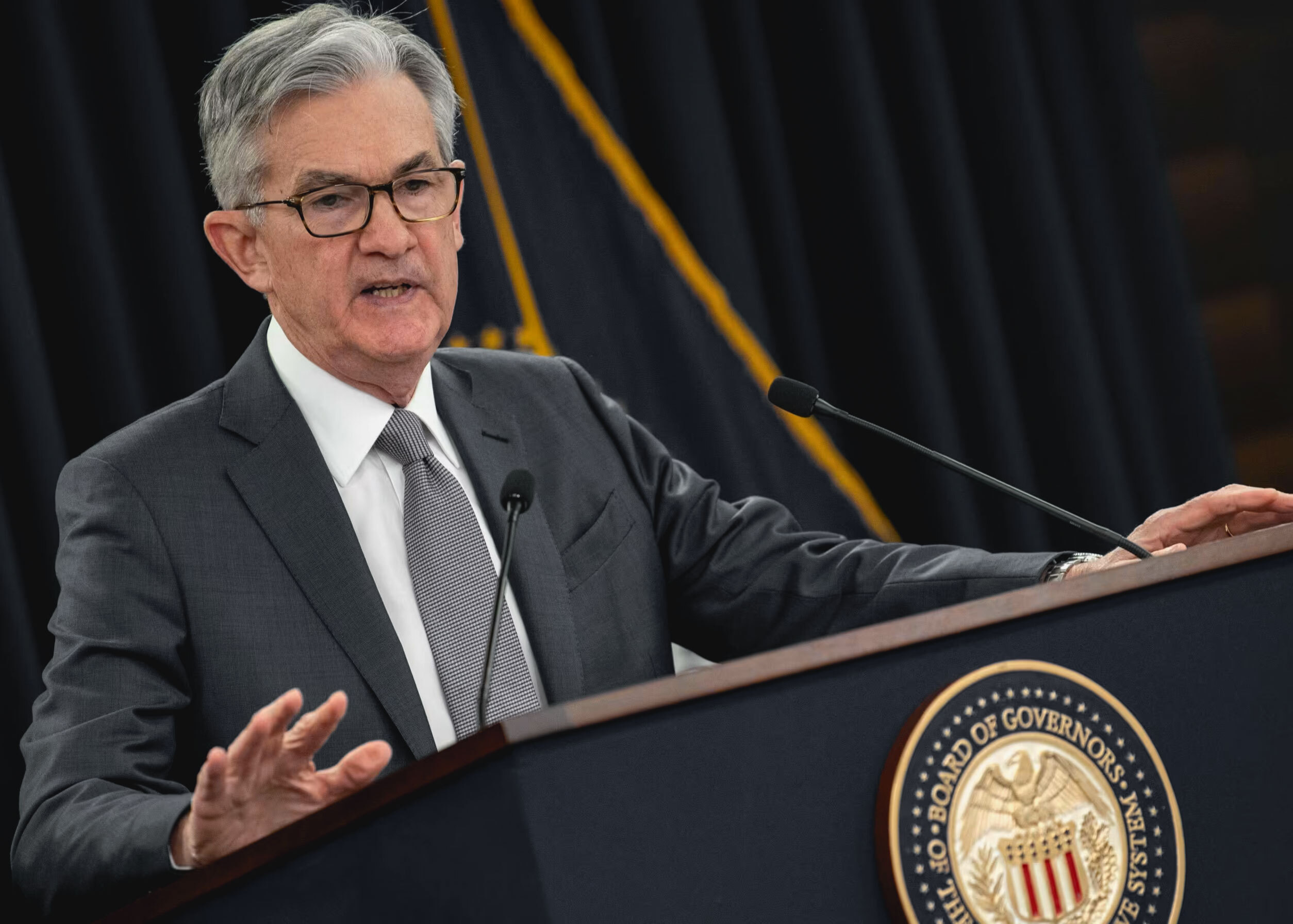

Major data releases from the US Federal Reserve within the span of 12th to 14th February are reported widely to have a broad impact on the US economy and global market. Let’s try to have a close look at the CPI and PPI news and other data releases one by one.
Consumer Price Index (CPI): February 12, 2025
On February 12, 2025, the CPI data for the previous month was released showing a 0.5% month-on-month growth. This has also pushed the annual CPI rate to 3.0%. Compared to the 2.9% CPI rate in December 2024, this reflects a minimal increase. Higher market prices of food and energy have been the major contributors to this substantial increase. CPI market implications have taken the headlines as the report is likely to showcase inflationary factors.
Producer Price Index (PPI): February 13, 2025
The Producer Price Index(PPI) has also experienced an increase of 0.4% in January 2025, according to the data released on February 13, 2025. The increase was a notch ahead of what the market expected. This along with CPI data released on the previous data shows clear trends of rising inflation, whether at the consumer or wholesale level.
Retail Sales Data: February 14, 2025
January US retail sales data was released on February 14, and keeping the same resilient momentum of releases in the last two days, it also showed a 0.3% month-on-month growth. Even the most conservative analysts will not fail to recognize the upbeat consumer sentiment from this retail sales data release, especially when rising prices could work as a deterrent.
A Closer Look at the Market Implications
The release of recent economic data, namely, CPI, PPI, unemployment figures, and retail sales brings us to a very complex scenario of mixed market sentiments. All these reports give rise to our concerns over inflation. On the other hand, there have been positive signals like the resilient employment scenario and steadily increasing consumer spending. Let’s go deeper into these factors, their market outcomes, and near-future probabilities.
Federal Interest Rate Strategy
The consistent increase in both CPI and PPI data points tells us that pressures of inflation have not yet subsided and the pressure may linger for a longer period than expected as of now. This is why it is less expected of the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates any time soon. Already most traders have postponed their expectations of a possible rate cut to September or even later.
The higher interest rate, not being vulnerable to any rate-cut decision can make the businesses and consumers suffer from higher borrowing costs. On the other hand, higher rates for consumer finance products like auto loans and credit cards can take a toll on consumer spending, especially in discreet categories such as travel, luxury items, and entertainment.
Volatile Reaction in Markets
Markets following the release of these data have already shown their reactions explicitly. Following the release of CPI data on February 12, the S&P 500 stocks experienced a sharp decline. The same was experienced by Nasdaq, despite its ride on the optimism around AI and top tech shares.
Bond markets, on the other hand, reflected the positive sides of these rate-cut expectations. Bonds continued to make higher yields making such fixed-investment options more lucrative compared to stocks. This further aggravated the pressure on the stock markets. Lastly, despite everything, the corporate earnings of many companies stayed on the growth curve, making the scenario cautious yet hopeful.
Increased Consumer Spending and Retail Sales
Despite the concerns over inflation, the retail sales figures in the U.S. grew 0.3% in January following a strong 0.8% increase just the previous month. This clearly shows that irrespective of higher prices and rising pressures of inflation, consumers still tend to spend more. Increased consumer spending explicitly showcased by these data releases benefitted e-commerce, sports goods, and home furnishing and improvement stores the most.
From such variance in consumer spending, it is evident that consumers tend to spend more selectively on purchases. While the sales of essential goods are having an upward boost, spending on luxury and high-value goods is steadily decreasing. This also shows the cost-conscious buying patterns of consumers at large. Last but not least, the threat of household debt is increasingly becoming a concern for consumer spending, especially because of the continuing interest rates.
Positive Signals from the Employment Market
The employment market as per the latest released data, has defied expectations and the number of jobless people has fallen to 213,000 in February. This clearly shows that businesses are not opting for layoffs.
On the downside, the growth of wages has reduced a little. The moderate wage growth in turn is likely to ease the inflation pressure to a certain extent.
A Quick Recap of the Most Affected Sectors

Not all sectors share the bruises and burns of these new data releases in the same way. While some sectors are likely to experience positive outcomes, there are others to struggle with negative indicators.
When it comes to the housing and real estate sector, higher mortgage rates can negatively impact home purchases creating further constraints on the demand and supply in the real estate sector. In the case of essential retail and consumer goods, there is a strong signal for better performance, but spending on high-value goods and luxury items can slow down. This can impact brands relying heavily on consumers from middle-income and upper-income groups.
Increased bond yields can slow down demand for tech stocks, particularly ones dependent heavily on institutional funding and venture capital for expanding to new markets and tech niches. Increased pricing for energies and raw materials in the manufacturing sector is imminent as inventory costs are increasing, as per the PPI data, released this month.
Ending Notes
Whatever outcome we come across following the release of the latest CPI, PPI, unemployment, and retail sales data showcases the complexity of an economic situation. The vulnerabilities to inflation remain a constant constraint resulting in continuous delaying of the interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve. While investors and traders continuously need to adjust to this emerging reality, the market volatility is not going to fade away anytime soon.